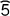
Dimensioning symbols replace text and are used to minimize language barriers. Many companies produce parts all over the world. A print made in the U.S.A. may be read in several different countries. The goal of using dimensioning symbols it to eliminate the need for language translation.
GD&T uses internationally accepted symbols that for the most part cross all language barriers. This enables the correct interpretation of drawing specifications without language translation. The following tables show the symbols that are used in GD&T. The symbols will be illustrated and explained as the learning material unfolds.
DIMENSIONING SYMBOLS
| Term | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Diameter | n |
| Spherical Diameter | Sn |
| Radius | R |
| Spherical Radius | SR |
| Reference Dimension | (8) |
| Counterbore / Spotface | v |
| Countersink | w |
| Number of Places | 4X |
| Depth / Deep | x |
| Dimension not to scale | 10 |
| Square (shape) | o |
| Arc Length | 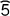 |
| Conical Taper | y |
| Slope | z |
| Symmetry | i |
GD&T GEOMETRIC CHARACTERISTIC SYMBOLS
| Tolerance Type | Characteristic | Symbol | |
|---|---|---|---|
| For individual features | Form | Straightness | u |
| Flatness | c | ||
| Circularity | e | ||
| Cylindricity | g | ||
| For individual or related features | Profile | Profile of a Line | k |
| Profile of a Surface | d | ||
| For related features | Orientation | Angularity | a |
| Perpendicularity | b | ||
| Parallelism | f | ||
| Location | Position | j | |
| Concentricity | r | ||
| Symmetry | i | ||
| Runout | Circular Runout | h | |
| Total Runout | t |
GD&T MATERIAL CONDITIONS
| Term | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Maximum Material Condition | m |
| Least Material Condition | l |
| Regardless of Feature Size | None |
ADDITIONAL GD&T SYMBOLS
| Term | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Basic Dimension |  |
| Between |  |
| Dimension Origin |  |
| All Around |  |
| Controlled Radius | CR |
| Statistical Tolerance |  |
| Projected Tolerance Zone | p |
| Regardless of feature size | s or None |
| Tangent Plane |  |
| Free State |  |
| Datum Feature | 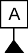 |
| Datum Target | 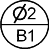 |
| Target Point |  |